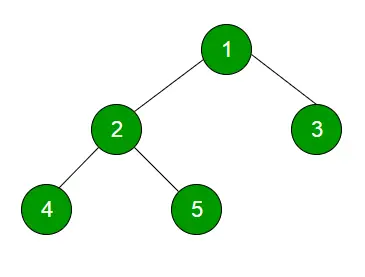
Обхід порядку рівня Техніка визначається як метод обходу дерева таким чином, що всі вузли, присутні на одному рівні, обходяться повністю перед обходом наступного рівня.
приклад:
Рекомендована практика Обхід порядку рівня Спробуйте!введення:
Вихід:
1
23
Чотири
Як працює Level Order Traversal?
Основна ідея обходу порядку рівнів полягає в обході всіх вузлів нижчого рівня перед переходом до будь-якого з вузлів вищого рівня. Це можна зробити будь-яким із наведених нижче способів.
- наївний (знаходження висоти дерева та проходження кожного рівня та друк вузлів цього рівня)
- ефективне використання черги.
Обхід порядку рівня (Наївний підхід):
знайти висота з дерева. Потім для кожного рівня запустіть рекурсивну функцію, зберігаючи поточну висоту. Щоразу, коли рівень вузла збігається, друкуйте цей вузол.
Нижче наведено реалізацію вищезазначеного підходу:
C++ // Recursive CPP program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree #include using namespace std; // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child class node { public: int data; node *left, *right; }; // Function prototypes void printCurrentLevel(node* root, int level); int height(node* node); node* newNode(int data); // Function to print level order traversal a tree void printLevelOrder(node* root) { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Print nodes at a current level void printCurrentLevel(node* root, int level) { if (root == NULL) return; if (level == 1) cout << root->даних<< ' '; else if (level>1) { printCurrentLevel(root->left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root->right, level - 1); } } // Обчислюємо 'висоту' дерева -- кількість // вузлів уздовж найдовшого шляху від кореневого вузла // до найдальшого листового вузла. int height(node* node) { if (node == NULL) return 0; else { // Обчислюємо висоту кожного піддерева int lheight = height(node->left); int rheight = height(node->right); // Використовуйте більший if (lheight> rheight) { return (lheight + 1); } else { return (справа + 1); } } } // Допоміжна функція, яка виділяє // новий вузол із заданими даними та // NULL лівим і правим покажчиками. node* newNode(int data) { node* Node = new node(); Node->data = дані; Node->left = NULL; Node->right = NULL; повернення (вузол); } // Код драйвера int main() { node* root = newNode(1); root->left = newNode(2); root->right = newNode(3); root->left->left = newNode(4); root->left->right = newNode(5); cout<< 'Level Order traversal of binary tree is
'; printLevelOrder(root); return 0; } // This code is contributed by rathbhupendra> C // Recursive C program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree #include #include // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child struct node { int data; struct node *left, *right; }; // Function prototypes void printCurrentLevel(struct node* root, int level); int height(struct node* node); struct node* newNode(int data); // Function to print level order traversal a tree void printLevelOrder(struct node* root) { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Print nodes at a current level void printCurrentLevel(struct node* root, int level) { if (root == NULL) return; if (level == 1) printf('%d ', root->дані); else if (рівень> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root->left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root->right, level - 1); } } // Обчислюємо 'висоту' дерева -- кількість // вузлів уздовж найдовшого шляху від кореневого вузла // до найдальшого листового вузла int height(struct node* node) { if (node == NULL) повертає 0; else { // Обчислюємо висоту кожного піддерева int lheight = height(node->left); int rheight = height(node->right); // Використовувати більший if (lheight> rheight) return (lheight + 1); else return (справа + 1); } } // Допоміжна функція, яка виділяє новий вузол із // заданими даними та NULL лівим і правим покажчиками. struct node* newNode(int data) { struct node* node = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); node->data = дані; node->left = NULL; node->right = NULL; повернення (вузол); } // Програма драйвера для перевірки вищевказаних функцій int main() { struct node* root = newNode(1); root->left = newNode(2); root->right = newNode(3); root->left->left = newNode(4); root->left->right = newNode(5); printf('Порядок проходження рівня бінарного дерева
'); printLevelOrder(корінь); повернути 0; }> Java // Recursive Java program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree // Class containing left and right child of current // node and key value class Node { int data; Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class BinaryTree { // Root of the Binary Tree Node root; public BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Function to print level order traversal of tree void printLevelOrder() { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Compute the 'height' of a tree -- the number of // nodes along the longest path from the root node // down to the farthest leaf node. int height(Node root) { if (root == null) return 0; else { // Compute height of each subtree int lheight = height(root.left); int rheight = height(root.right); // use the larger one if (lheight>rheight) повернення (lheight + 1); else return (праворуч + 1); } } // Друк вузлів на поточному рівні void printCurrentLevel(Node root, int level) { if (root == null) return; if (рівень == 1) System.out.print(root.data + ' '); else if (рівень> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, рівень - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, рівень - 1); } } // Програма драйвера для тестування вищезазначених функцій public static void main(String args[]) { BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree(); tree.root = новий вузол (1); tree.root.left = новий вузол (2); tree.root.right = новий вузол (3); tree.root.left.left = новий вузол (4); tree.root.left.right = новий вузол (5); System.out.println('Обхід порядку рівня' + 'бінарне дерево є '); tree.printLevelOrder(); } }> Python # Recursive Python program for level # order traversal of Binary Tree # A node structure class Node: # A utility function to create a new node def __init__(self, key): self.data = key self.left = None self.right = None # Function to print level order traversal of tree def printLevelOrder(root): h = height(root) for i in range(1, h+1): printCurrentLevel(root, i) # Print nodes at a current level def printCurrentLevel(root, level): if root is None: return if level == 1: print(root.data, end=' ') elif level>1: printCurrentLevel(root.left, level-1) printCurrentLevel(root.right, level-1) # Обчислити висоту дерева — кількість вузлів # уздовж найдовшого шляху від кореневого вузла до # найдальшого аркуша node def height(node): якщо вузол None: повертає 0 else: # Обчислює висоту кожного піддерева lheight = height(node.left) rheight = height(node.right) # Використовує більший, якщо lheight> rheight: return lheight+1 else: return rheight+1 # Програма драйвера для перевірки вищезазначеної функції, якщо __name__ == '__main__': root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root. left.left = Node(4) root.left.right = Node(5) print('Порядок проходження рівня бінарного дерева -') printLevelOrder(root) # Цей код створено Ніхілом Кумаром Сінгхом(nickzuck_007)> C# // Recursive c# program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree using System; // Class containing left and right // child of current node and key value public class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class GFG { // Root of the Binary Tree public Node root; public void BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Function to print level order // traversal of tree public virtual void printLevelOrder() { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) { printCurrentLevel(root, i); } } // Compute the 'height' of a tree -- // the number of nodes along the longest // path from the root node down to the // farthest leaf node. public virtual int height(Node root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } else { // Compute height of each subtree int lheight = height(root.left); int rheight = height(root.right); // use the larger one if (lheight>справа) { return (lвисота + 1); } else { return (справа + 1); } } } // Друк вузлів на поточному рівні public virtual void printCurrentLevel(Node root, int level) { if (root == null) { return; } if (level == 1) { Console.Write(root.data + ' '); } else if (рівень> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, рівень - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, рівень - 1); } } // Код драйвера public static void Main(string[] args) { GFG tree = new GFG(); tree.root = новий вузол (1); tree.root.left = новий вузол (2); tree.root.right = новий вузол (3); tree.root.left.left = новий вузол (4); tree.root.left.right = новий вузол (5); Console.WriteLine('Обхід порядку рівня ' + 'бінарного дерева є '); tree.printLevelOrder(); } } // Цей код створено Shrikant13> Javascript // Recursive javascript program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree // Class containing left and right child of current // node and key value class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Root of the Binary Tree var root= null; // Function to print level order traversal of tree function printLevelOrder() { var h = height(root); var i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Compute the 'height' of a tree -- the number // of nodes along the longest path // from the root node down to the farthest leaf node. function height(root) { if (root == null) return 0; else { // Compute height of each subtree var lheight = height(root.left); var rheight = height(root.right); // Use the larger one if (lheight>rheight) повернення (lheight + 1); else return (праворуч + 1); } } // Друк вузлів на поточному рівні function printCurrentLevel(root , level) { if (root == null) return; якщо (рівень == 1) console.log(root.data + ' '); else if (рівень> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, рівень - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, рівень - 1); } } // Програма драйвера для перевірки вищезазначених функцій root = new Node(1); root.left = новий вузол (2); root.right = новий вузол (3); root.left.left = новий вузол (4); root.left.right = новий вузол (5); console.log('Порядок проходження рівня бінарного дерева є '); printLevelOrder(); // Цей код створено umadevi9616>>>
Вихід Level Order traversal of binary tree is 1 2 3 4 5>
Часова складність: O(N), де N – кількість вузлів у перекошеному дереві.
Допоміжний простір: O(1) Якщо розглядається стек рекурсії, використовується простір O(N).
отримати поточну дату в java
За допомогою обходу порядку рівня Черга
Нам потрібно відвідати вузли нижчого рівня перед будь-яким вузлом вищого рівня, ця ідея дуже схожа на ідею черги. Просунути вузли нижчого рівня в черзі. Коли відвідується будь-який вузол, витягніть цей вузол із черги та помістіть дочірній елемент цього вузла в чергу.
Це гарантує, що вузол нижчого рівня відвідується перед будь-яким вузлом вищого рівня.
Нижче наведено реалізацію вищезазначеного підходу:
C++ // C++ program to print level order traversal #include using namespace std; // A Binary Tree Node struct Node { int data; struct Node *left, *right; }; // Iterative method to find height of Binary Tree void printLevelOrder(Node* root) { // Base Case if (root == NULL) return; // Create an empty queue for level order traversal queueq; // Ставимо кореневу чергу та ініціалізуємо висоту q.push(root); while (q.empty() == false) { // Роздрукувати початок черги та видалити його з черги Node* node = q.front(); cout<< node->даних<< ' '; q.pop(); // Enqueue left child if (node->зліва != NULL) q.push(node->left); // Поставити в чергу правий дочірній елемент if (node->right != NULL) q.push(node->right); } } // Допоміжна функція для створення нового вузла дерева Node* newNode(int data) { Node* temp = new Node; temp->data = дані; temp->left = temp->right = NULL; зворотна температура; } // Програма драйвера для тестування вищезазначених функцій int main() { // Створимо двійкове дерево, показане на схемі вище Node* root = newNode(1); root->left = newNode(2); root->right = newNode(3); root->left->left = newNode(4); root->left->right = newNode(5); cout<< 'Level Order traversal of binary tree is
'; printLevelOrder(root); return 0; }> C // Iterative Queue based C program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree #include #include #define MAX_Q_SIZE 500 // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child struct node { int data; struct node* left; struct node* right; }; // Function prototypes struct node** createQueue(int*, int*); void enQueue(struct node**, int*, struct node*); struct node* deQueue(struct node**, int*); // Given a binary tree, print its nodes in level order // using array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder(struct node* root) { int rear, front; struct node** queue = createQueue(&front, &rear); struct node* temp_node = root; while (temp_node) { printf('%d ', temp_node->дані); // Поставити в чергу лівого дочірнього елемента if (temp_node->left) enQueue(queue, &rear, temp_node->left); // Поставити в чергу правий дочірній елемент if (temp_node->right) enQueue(queue, &rear, temp_node->right); // Зняти вузол із черги та зробити його temp_node temp_node = deQueue(queue, &front); } } // Допоміжні функції struct node** createQueue(int* front, int* rear) { struct node** queue = (struct node**)malloc( sizeof(struct node*) * MAX_Q_SIZE); *передня = *задня = 0; черга повернення; } void enQueue(struct node** queue, int* rear, struct node* new_node) { queue[*rear] = new_node; (*задній)++; } struct node* deQueue(struct node** queue, int* front) { (*front)++; черга повернення [*front - 1]; } // Допоміжна функція, яка виділяє новий вузол із // заданими даними та NULL лівим і правим покажчиками. struct node* newNode(int data) { struct node* node = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); node->data = дані; node->left = NULL; node->right = NULL; повернення (вузол); } // Програма драйвера для перевірки вищевказаних функцій int main() { struct node* root = newNode(1); root->left = newNode(2); root->right = newNode(3); root->left->left = newNode(4); root->left->right = newNode(5); printf('Порядок проходження рівня бінарного дерева
'); printLevelOrder(корінь); повернути 0; }> Java // Iterative Queue based Java program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; // Class to represent Tree node class Node { int data; Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = null; right = null; } } // Class to print Level Order Traversal class BinaryTree { Node root; // Given a binary tree. Print // its nodes in level order // using array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder() { Queuequeue = новий LinkedList(); queue.add(корінь); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { // poll() видаляє поточну голову. Вузол tempNode = queue.poll(); System.out.print(tempNode.data + ' '); // Поставте в чергу лівого дочірнього елемента if (tempNode.left != null) { queue.add(tempNode.left); } // Поставити в чергу правого дочірнього елемента if (tempNode.right != null) { queue.add(tempNode.right); } } } public static void main(String args[]) { // Створення двійкового дерева та введення // вузлів BinaryTree tree_level = new BinaryTree(); tree_level.root = новий вузол (1); tree_level.root.left = новий вузол (2); tree_level.root.right = новий вузол(3); tree_level.root.left.left = новий вузол(4); tree_level.root.left.right = новий вузол(5); System.out.println('Порядок проходження рівня бінарного дерева - '); tree_level.printLevelOrder(); } }> Python # Python program to print level # order traversal using Queue # A node structure class Node: # A utility function to create a new node def __init__(self, key): self.data = key self.left = None self.right = None # Iterative Method to print the # height of a binary tree def printLevelOrder(root): # Base Case if root is None: return # Create an empty queue # for level order traversal queue = [] # Enqueue Root and initialize height queue.append(root) while(len(queue)>0): # Надрукувати початок черги та # видалити його з черги print(queue[0].data, end=' ') node = queue.pop(0) # Поставити в чергу лівого дочірнього елемента, якщо node.left не є None: queue.append(node.left) # Поставити в чергу правого дочірнього елемента, якщо node.right не є None: queue.append(node.right) # Програма драйвера для перевірки вищезазначеної функції, якщо __name__ == '__main__': root = Node(1 ) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root.left.left = Node(4) root.left.right = Node(5) print('Порядок проходження рівнів бінарного дерева - ') printLevelOrder(root) # Цей код надав Нікіл Кумар Сінгх(nickzuck_007)> C# // Iterative Queue based C# program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree using System; using System.Collections.Generic; // Class to represent Tree node public class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = null; right = null; } } // Class to print Level Order Traversal public class BinaryTree { Node root; // Given a binary tree. Print // its nodes in level order using // array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder() { Queuequeue = нова черга(); queue.Enqueue(корінь); while (queue.Count != 0) { Node tempNode = queue.Dequeue(); Console.Write(tempNode.data + ' '); // Поставити лівого дочірнього елемента в чергу if (tempNode.left != null) { queue.Enqueue(tempNode.left); } // Поставити в чергу правого дочірнього елемента if (tempNode.right != null) { queue.Enqueue(tempNode.right); } } } // Код драйвера public static void Main() { // Створення двійкового дерева та введення // вузлів BinaryTree tree_level = new BinaryTree(); tree_level.root = новий вузол (1); tree_level.root.left = новий вузол (2); tree_level.root.right = новий вузол(3); tree_level.root.left.left = новий вузол(4); tree_level.root.left.right = новий вузол(5); Console.WriteLine('Обхід порядку рівня ' + 'бінарного дерева є - '); tree_level.printLevelOrder(); } } // Цей код надав PrinciRaj1992> Javascript class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Class to represent a deque (double-ended queue) class Deque { constructor() { this.queue = []; } // Method to add an element to the end of the queue enqueue(item) { this.queue.push(item); } // Method to remove and return the first element of the queue dequeue() { return this.queue.shift(); } // Method to check if the queue is empty isEmpty() { return this.queue.length === 0; } } // Function to perform level order traversal of a binary tree function printLevelOrder(root) { // Create a deque to store nodes for traversal const queue = new Deque(); // Add the root node to the queue queue.enqueue(root); // Continue traversal until the queue is empty while (!queue.isEmpty()) { // Remove and get the first node from the queue const tempNode = queue.dequeue(); // Print the data of the current node console.log(tempNode.data + ' '); // Enqueue the left child if it exists if (tempNode.left !== null) { queue.enqueue(tempNode.left); } // Enqueue the right child if it exists if (tempNode.right !== null) { queue.enqueue(tempNode.right); } } } // Create a binary tree and enter the nodes const root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); // Print the level order traversal of the binary tree console.log('Level order traversal of binary tree is - '); printLevelOrder(root);> Вихід
Допоміжний простір: O(N), де N – кількість вузлів у бінарному дереві.