Дерево AVL:
Дерево AVL є самобалансуючим бінарним деревом пошуку ( BST ), де різниця між висотами лівого та правого піддерев не може перевищувати один для всіх вузлів.
Приклад дерева AVL:
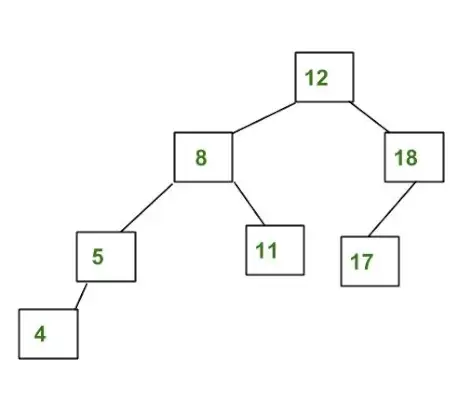
Наведене вище дерево є AVL, оскільки різниця між висотами лівого та правого піддерев для кожного вузла менше або дорівнює 1.
Приклад дерева, яке НЕ є деревом AVL:

Наведене вище дерево не є AVL, оскільки різниця між висотою лівого та правого піддерев для 8 і 12 більша за 1.
хто винайшов школу
Чому AVL Trees?
Більшість операцій BST (наприклад, пошук, макс., мінім., вставка, видалення... тощо) займають O(h) час де ч висота BST. Вартість цих операцій може стати O(n) для перекошене двійкове дерево . Якщо ми переконаємося, що висота дерева залишається O(log(n)) після кожної вставки та видалення ми можемо гарантувати верхню межу O(log(n)) для всіх цих операцій. Висота дерева AVL завжди дорівнює O(log(n)) де п це кількість вузлів у дереві.
Вставка у дереві AVL:
Щоб переконатися, що дане дерево залишається AVL після кожної вставки, ми повинні розширити стандартну операцію вставки BST, щоб виконати деяку перебалансування.
Нижче наведено дві основні операції, які можна виконати, щоб збалансувати BST без порушення властивості BST (клавіші (ліворуч)
- Обертання вліво
- Обертання вправо
T1, T2 and T3 are subtrees of the tree, rooted with y (on the left side) or x (on the right side) y x / Right Rotation / x T3 - - - - - - ->T1 і / <- - - - - - - / T1 T2 Left Rotation T2 T3 Keys in both of the above trees follow the following order keys(T1) < key(x) < keys(T2) < key(y) < keys(T3) So BST property is not violated anywhere.>Рекомендована практика Вставка дерева AVL Спробуйте!
Кроки для вставки:
Нехай щойно вставлений вузол буде в
- Виконати стандарт BST вставка для в .
- Починаючи з в , подорожуйте вгору та знайдіть перший незбалансований вузол . Дозволяти с бути першим незбалансованим вузлом, і бути дитина з с що йде на шляху від в до с і x бути онука з с що йде на шляху від в до с .
- Знову збалансуйте дерево, виконавши відповідні обертання на піддереві, яке має коріння с. Може бути 4 можливі випадки, які потрібно розглядати як x,y і с можна організувати 4 способами.
- Нижче наведено 4 можливі схеми:
- y є лівим нащадком z і x є лівим нащадком y (лівий лівий регістр)
- y є лівим нащадком z, а x є правим нащадком y (лівий правий регістр)
- y є правим нащадком z і x є правим нащадком y (правий регістр)
- y є правим нащадком z, а x є лівим нащадком y (правий лівий регістр)
Нижче наведено операції, які необхідно виконати у згаданих вище 4 випадках. У всіх випадках нам потрібно лише повторний баланс піддерево вкорінене с с і повне дерево стає збалансованим, оскільки висота піддерева (Після відповідних обертань) корениться з с стає таким же, яким був до введення.
1. Лівий лівий регістр
T1, T2, T3 and T4 are subtrees. z y / / y T4 Right Rotate (z) x z / - - - - - - - - ->/ / x T3 T1 T2 T3 T4 / T1 T2>
2. Лівий правий регістр
z z x / / / y T4 Left Rotate (y) x T4 Right Rotate(z) y z / - - - - - - - - ->/ - - - - - - - -> / / T1 x y T3 T1 T2 T3 T4 / / T2 T3 T1 T2>
3. Right Right Case
z y / / T1 y Left Rotate(z) z x / - - - - - - - ->/ / T2 x T1 T2 T3 T4 / T3 T4>
4. Правий лівий регістр
z z x / / / T1 y Right Rotate (y) T1 x Left Rotate(z) z y / - - - - - - - - ->/ - - - - - - - -> / / x T4 T2 y T1 T2 T3 T4 / / T2 T3 T3 T4>
Ілюстрація вставки в дерево AVL





Підхід:
Ідея полягає в тому, щоб використовувати рекурсивну вставку BST, після вставки ми отримуємо вказівники на всіх предків одного за одним у спосіб знизу вгору. Тому нам не потрібен батьківський покажчик, щоб подорожувати вгору. Сам рекурсивний код подорожує вгору та відвідує всіх предків щойно вставленого вузла.
Щоб реалізувати ідею, виконайте наведені нижче кроки:
Підручник мовою програмування java
- Виконайте нормальний режим Вставка BST.
- Поточний вузол має бути одним із предків щойно вставленого вузла. Оновити висота поточного вузла.
- Отримайте коефіцієнт балансу (висота лівого піддерева – висота правого піддерева) поточного вузла.
- Якщо коефіцієнт балансу більше, ніж 1, то поточний вузол незбалансований, і ми або в Ліворуч Лівий регістр або лівий правий регістр . Щоб перевірити, чи це так лівий лівий регістр чи ні, порівняйте щойно вставлений ключ із ключем у лівий корінь піддерева .
- Якщо коефіцієнт балансу менше ніж -1 , тоді поточний вузол є незбалансованим, і ми знаходимося або в правому правому випадку, або в правому лівому випадку. Щоб перевірити, чи це регістр Right Right чи ні, порівняйте щойно вставлений ключ із ключем у корені правого піддерева.
Нижче наведено реалізацію вищезазначеного підходу:
C++14
// C++ program to insert a node in AVL tree> #include> using> namespace> std;> > // An AVL tree node> class> Node> {> >public>:> >int> key;> >Node *left;> >Node *right;> >int> height;> };> > // A utility function to get the> // height of the tree> int> height(Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> N->висота;> }> > // A utility function to get maximum> // of two integers> int> max(>int> a,>int> b)> {> >return> (a>б)? а : б;> }> > /* Helper function that allocates a> >new node with the given key and> >NULL left and right pointers. */> Node* newNode(>int> key)> {> >Node* node =>new> Node();> >node->ключ = ключ;> >node->зліва = NULL;> >node->справа = NULL;> >node->висота = 1;>// new node is initially> >// added at leaf> >return>(node);> }> > // A utility function to right> // rotate subtree rooted with y> // See the diagram given above.> Node *rightRotate(Node *y)> {> >Node *x = y->зліва;> >Node *T2 = x->справа;> > >// Perform rotation> >x->справа = у;> >y->зліва = Т2;> > >// Update heights> >y->висота = max(висота(y->ліворуч),> >height(y->правильно)) + 1;> >x->висота = max(висота(x->ліворуч),> >height(x->правильно)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> }> > // A utility function to left> // rotate subtree rooted with x> // See the diagram given above.> Node *leftRotate(Node *x)> {> >Node *y = x->справа;> >Node *T2 = y->зліва;> > >// Perform rotation> >y->зліва = x;> >x->справа = Т2;> > >// Update heights> >x->висота = max(висота(x->ліворуч),> >height(x->правильно)) + 1;> >y->висота = max(висота(y->ліворуч),> >height(y->правильно)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> }> > // Get Balance factor of node N> int> getBalance(Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> height(N->ліворуч) - висота (N->праворуч);> }> > // Recursive function to insert a key> // in the subtree rooted with node and> // returns the new root of the subtree.> Node* insert(Node* node,>int> key)> {> >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node == NULL)> >return>(newNode(key));> > >if> (key key)> >node->ліворуч = вставити (вузол->ліворуч, ключ);> >else> if> (key>вузол->ключ)> >node->праворуч = вставити (вузол->праворуч, ключ);> >else> // Equal keys are not allowed in BST> >return> node;> > >/* 2. Update height of this ancestor node */> >node->висота = 1 + max(висота(вузол->ліворуч),> >height(node->правильно));> > >/* 3. Get the balance factor of this ancestor> >node to check whether this node became> >unbalanced */> >int> balance = getBalance(node);> > >// If this node becomes unbalanced, then> >// there are 4 cases> > >// Left Left Case> >if> (balance>1 && клавіша ліворуч->клавіша)> >return> rightRotate(node);> > >// Right Right Case> >if> (balance node->вправо->клавіша)> >return> leftRotate(node);> > >// Left Right Case> >if> (balance>1 && клавіша> вузол->ліворуч->клавіша)> >{> >node->ліворуч = leftRotate(node->left);> >return> rightRotate(node);> >}> > >// Right Left Case> >if> (balance <-1 && key right->ключ)> >{> >node->right = rightRotate(node->right);> >return> leftRotate(node);> >}> > >/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */> >return> node;> }> > // A utility function to print preorder> // traversal of the tree.> // The function also prints height> // of every node> void> preOrder(Node *root)> {> >if>(root != NULL)> >{> >cout ' '; preOrder(root->ліворуч); preOrder(root->right); } } // Код драйвера int main() { Node *root = NULL; /* Побудова дерева, наведеного на малюнку вище */ root = insert(root, 10); корінь = вставити (корінь, 20); корінь = вставити (корінь, 30); корінь = вставка (корінь, 40); корінь = вставка (корінь, 50); корінь = вставити (корінь, 25); /* Побудоване дерево AVL буде 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ cout<< 'Preorder traversal of the ' 'constructed AVL tree is
'; preOrder(root); return 0; } // This code is contributed by // rathbhupendra> |
>
>
C
// C program to insert a node in AVL tree> #include> #include> > // An AVL tree node> struct> Node> {> >int> key;> >struct> Node *left;> >struct> Node *right;> >int> height;> };> > // A utility function to get the height of the tree> int> height(>struct> Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> N->висота;> }> > // A utility function to get maximum of two integers> int> max(>int> a,>int> b)> {> >return> (a>б)? а : б;> }> > /* Helper function that allocates a new node with the given key and> >NULL left and right pointers. */> struct> Node* newNode(>int> key)> {> >struct> Node* node = (>struct> Node*)> >malloc>(>sizeof>(>struct> Node));> >node->ключ = ключ;> >node->зліва = NULL;> >node->справа = NULL;> >node->висота = 1;>// new node is initially added at leaf> >return>(node);> }> > // A utility function to right rotate subtree rooted with y> // See the diagram given above.> struct> Node *rightRotate(>struct> Node *y)> {> >struct> Node *x = y->зліва;> >struct> Node *T2 = x->справа;> > >// Perform rotation> >x->справа = у;> >y->зліва = Т2;> > >// Update heights> >y->висота = max(висота(y->ліворуч),> >height(y->правильно)) + 1;> >x->висота = max(висота(x->ліворуч),> >height(x->правильно)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> }> > // A utility function to left rotate subtree rooted with x> // See the diagram given above.> struct> Node *leftRotate(>struct> Node *x)> {> >struct> Node *y = x->справа;> >struct> Node *T2 = y->зліва;> > >// Perform rotation> >y->зліва = x;> >x->справа = Т2;> > >// Update heights> >x->висота = max(висота(x->ліворуч),> >height(x->правильно)) + 1;> >y->висота = max(висота(y->ліворуч),> >height(y->правильно)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> }> > // Get Balance factor of node N> int> getBalance(>struct> Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> height(N->ліворуч) - висота (N->праворуч);> }> > // Recursive function to insert a key in the subtree rooted> // with node and returns the new root of the subtree.> struct> Node* insert(>struct> Node* node,>int> key)> {> >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node == NULL)> >return>(newNode(key));> > >if> (key key)> >node->ліворуч = вставити (вузол->ліворуч, ключ);> >else> if> (key>вузол->ключ)> >node->праворуч = вставити (вузол->праворуч, ключ);> >else> // Equal keys are not allowed in BST> >return> node;> > >/* 2. Update height of this ancestor node */> >node->висота = 1 + max(висота(вузол->ліворуч),> >height(node->правильно));> > >/* 3. Get the balance factor of this ancestor> >node to check whether this node became> >unbalanced */> >int> balance = getBalance(node);> > >// If this node becomes unbalanced, then> >// there are 4 cases> > >// Left Left Case> >if> (balance>1 && клавіша ліворуч->клавіша)> >return> rightRotate(node);> > >// Right Right Case> >if> (balance node->вправо->клавіша)> >return> leftRotate(node);> > >// Left Right Case> >if> (balance>1 && клавіша> вузол->ліворуч->клавіша)> >{> >node->лівий = лівий поворот (вузол->ліворуч);> >return> rightRotate(node);> >}> > >// Right Left Case> >if> (balance <-1 && key right->ключ)> >{> >node->right = rightRotate(node->right);> >return> leftRotate(node);> >}> > >/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */> >return> node;> }> > // A utility function to print preorder traversal> // of the tree.> // The function also prints height of every node> void> preOrder(>struct> Node *root)> {> >if>(root != NULL)> >{> >printf>(>'%d '>, root->ключ);> >preOrder(root->ліворуч);> >preOrder(root->праворуч);> >}> }> > /* Driver program to test above function*/> int> main()> {> >struct> Node *root = NULL;> > >/* Constructing tree given in the above figure */> >root = insert(root, 10);> >root = insert(root, 20);> >root = insert(root, 30);> >root = insert(root, 40);> >root = insert(root, 50);> >root = insert(root, 25);> > >/* The constructed AVL Tree would be> >30> >/> >20 40> >/> >10 25 50> >*/> > >printf>(>'Preorder traversal of the constructed AVL'> >' tree is
'>);> >preOrder(root);> > >return> 0;> }> |
метод підрядка java
>
>
Java
// Java program for insertion in AVL Tree> class> Node {> >int> key, height;> >Node left, right;> > >Node(>int> d) {> >key = d;> >height =>1>;> >}> }> > class> AVLTree {> > >Node root;> > >// A utility function to get the height of the tree> >int> height(Node N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0>;> > >return> N.height;> >}> > >// A utility function to get maximum of two integers> >int> max(>int> a,>int> b) {> >return> (a>б) ? а : б;> >}> > >// A utility function to right rotate subtree rooted with y> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node rightRotate(Node y) {> >Node x = y.left;> >Node T2 = x.right;> > >// Perform rotation> >x.right = y;> >y.left = T2;> > >// Update heights> >y.height = max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) +>1>;> >x.height = max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) +>1>;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> >}> > >// A utility function to left rotate subtree rooted with x> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node leftRotate(Node x) {> >Node y = x.right;> >Node T2 = y.left;> > >// Perform rotation> >y.left = x;> >x.right = T2;> > >// Update heights> >x.height = max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) +>1>;> >y.height = max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) +>1>;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> >}> > >// Get Balance factor of node N> >int> getBalance(Node N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0>;> > >return> height(N.left) - height(N.right);> >}> > >Node insert(Node node,>int> key) {> > >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node ==>null>)> >return> (>new> Node(key));> > >if> (key node.left = insert(node.left, key); else if (key>node.key) node.right = вставити(node.right, ключ); else // дублікати ключів не дозволені return node; /* 2. Оновити висоту цього вузла-попередника */ node.height = 1 + max(height(node.left), height(node.right)); /* 3. Отримати коефіцієнт балансу цього вузла-предка, щоб перевірити, чи цей вузол став незбалансованим */ int balance = getBalance(node); // Якщо цей вузол стає незбалансованим, тоді є // 4 випадки Ліворуч Ліворуч Регістр якщо (баланс> 1 && клавіша повернення rightRotate(вузол); // Правий Правий регістр якщо (баланс<-1 && key>node.right.key) return leftRotate(node); // Ліворуч Праворуч, якщо (баланс> 1 && ключ> node.left.key) { node.left = leftRotate(node.left); повернути вправоRotate(вузол); } // Правий лівий регістр if (баланс<-1 && key node.right = rightRotate(node.right); return leftRotate(node); } /* return the (unchanged) node pointer */ return node; } // A utility function to print preorder traversal // of the tree. // The function also prints height of every node void preOrder(Node node) { if (node != null) { System.out.print(node.key + ' '); preOrder(node.left); preOrder(node.right); } } public static void main(String[] args) { AVLTree tree = new AVLTree(); /* Constructing tree given in the above figure */ tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 40); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 25); /* The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ System.out.println('Preorder traversal' + ' of constructed tree is : '); tree.preOrder(tree.root); } } // This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal> |
>
>
Python3
# Python code to insert a node in AVL tree> > # Generic tree node class> class> TreeNode(>object>):> >def> __init__(>self>, val):> >self>.val>=> val> >self>.left>=> None> >self>.right>=> None> >self>.height>=> 1> > # AVL tree class which supports the> # Insert operation> class> AVL_Tree(>object>):> > ># Recursive function to insert key in> ># subtree rooted with node and returns> ># new root of subtree.> >def> insert(>self>, root, key):> > ># Step 1 - Perform normal BST> >if> not> root:> >return> TreeNode(key)> >elif> key root.left = self.insert(root.left, key) else: root.right = self.insert(root.right, key) # Step 2 - Update the height of the # ancestor node root.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(root.left), self.getHeight(root.right)) # Step 3 - Get the balance factor balance = self.getBalance(root) # Step 4 - If the node is unbalanced, # then try out the 4 cases # Case 1 - Left Left if balance>1 і клавіша return self.rightRotate(root) # Випадок 2 - Вправо Право, якщо баланс<-1 and key>root.right.val: return self.leftRotate(root) # Випадок 3 - Left Right if balance> 1 and key> root.left.val: root.left = self.leftRotate(root.left) return self.rightRotate(root ) # Випадок 4 - Праворуч Ліворуч, якщо баланс<-1 and key root.right = self.rightRotate(root.right) return self.leftRotate(root) return root def leftRotate(self, z): y = z.right T2 = y.left # Perform rotation y.left = z z.right = T2 # Update heights z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left), self.getHeight(z.right)) y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left), self.getHeight(y.right)) # Return the new root return y def rightRotate(self, z): y = z.left T3 = y.right # Perform rotation y.right = z z.left = T3 # Update heights z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left), self.getHeight(z.right)) y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left), self.getHeight(y.right)) # Return the new root return y def getHeight(self, root): if not root: return 0 return root.height def getBalance(self, root): if not root: return 0 return self.getHeight(root.left) - self.getHeight(root.right) def preOrder(self, root): if not root: return print('{0} '.format(root.val), end='') self.preOrder(root.left) self.preOrder(root.right) # Driver program to test above function myTree = AVL_Tree() root = None root = myTree.insert(root, 10) root = myTree.insert(root, 20) root = myTree.insert(root, 30) root = myTree.insert(root, 40) root = myTree.insert(root, 50) root = myTree.insert(root, 25) '''The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50''' # Preorder Traversal print('Preorder traversal of the', 'constructed AVL tree is') myTree.preOrder(root) print() # This code is contributed by Ajitesh Pathak> |
>
>
C#
диспетчер завдань для linux
// C# program for insertion in AVL Tree> using> System;> > class> Node> {> >public> int> key, height;> >public> Node left, right;> > >public> Node(>int> d)> >{> >key = d;> >height = 1;> >}> }> > public> class> AVLTree> {> > >Node root;> > >// A utility function to get> >// the height of the tree> >int> height(Node N)> >{> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0;> > >return> N.height;> >}> > >// A utility function to get> >// maximum of two integers> >int> max(>int> a,>int> b)> >{> >return> (a>б) ? а : б;> >}> > >// A utility function to right> >// rotate subtree rooted with y> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node rightRotate(Node y)> >{> >Node x = y.left;> >Node T2 = x.right;> > >// Perform rotation> >x.right = y;> >y.left = T2;> > >// Update heights> >y.height = max(height(y.left),> >height(y.right)) + 1;> >x.height = max(height(x.left),> >height(x.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> >}> > >// A utility function to left> >// rotate subtree rooted with x> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node leftRotate(Node x)> >{> >Node y = x.right;> >Node T2 = y.left;> > >// Perform rotation> >y.left = x;> >x.right = T2;> > >// Update heights> >x.height = max(height(x.left),> >height(x.right)) + 1;> >y.height = max(height(y.left),> >height(y.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> >}> > >// Get Balance factor of node N> >int> getBalance(Node N)> >{> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0;> > >return> height(N.left) - height(N.right);> >}> > >Node insert(Node node,>int> key)> >{> > >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node ==>null>)> >return> (>new> Node(key));> > >if> (key node.left = insert(node.left, key); else if (key>node.key) node.right = вставити(node.right, ключ); else // дублікати ключів не дозволені return node; /* 2. Оновити висоту цього вузла-попередника */ node.height = 1 + max(height(node.left), height(node.right)); /* 3. Отримати коефіцієнт балансу цього вузла-предка, щоб перевірити, чи цей вузол став незбалансованим */ int balance = getBalance(node); // Якщо цей вузол стає незбалансованим, тоді є // 4 випадки Left Left Case if (balance> 1 && key return rightRotate(node); // Right Right Case if (balance node.right.key) return leftRotate(node) ; // Left Right Case if (balance> 1 && key> node.left.key) { node.left = leftRotate(node.left); } // Right Left Case if (balance<-1 && key < node.right.key) { node.right = rightRotate(node.right); return leftRotate(node); } /* return the (unchanged) node pointer */ return node; } // A utility function to print preorder traversal // of the tree. // The function also prints height of every node void preOrder(Node node) { if (node != null) { Console.Write(node.key + ' '); preOrder(node.left); preOrder(node.right); } } // Driver code public static void Main(String[] args) { AVLTree tree = new AVLTree(); /* Constructing tree given in the above figure */ tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 40); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 25); /* The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ Console.Write('Preorder traversal' + ' of constructed tree is : '); tree.preOrder(tree.root); } } // This code has been contributed // by PrinciRaj1992> |
>
>
Javascript
> > >// JavaScript program for insertion in AVL Tree> >class Node {> >constructor(d) {> >this>.key = d;> >this>.height = 1;> >this>.left =>null>;> >this>.right =>null>;> >}> >}> > >class AVLTree {> >constructor() {> >this>.root =>null>;> >}> > >// A utility function to get> >// the height of the tree> >height(N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)>return> 0;> > >return> N.height;> >}> > >// A utility function to get> >// maximum of two integers> >max(a, b) {> >return> a>b ? а : б;> >}> > >// A utility function to right> >// rotate subtree rooted with y> >// See the diagram given above.> >rightRotate(y) {> >var> x = y.left;> >var> T2 = x.right;> > >// Perform rotation> >x.right = y;> >y.left = T2;> > >// Update heights> >y.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(y.left),> >this>.height(y.right)) + 1;> >x.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(x.left),> >this>.height(x.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> >}> > >// A utility function to left> >// rotate subtree rooted with x> >// See the diagram given above.> >leftRotate(x) {> >var> y = x.right;> >var> T2 = y.left;> > >// Perform rotation> >y.left = x;> >x.right = T2;> > >// Update heights> >x.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(x.left),> >this>.height(x.right)) + 1;> >y.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(y.left),> >this>.height(y.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> >}> > >// Get Balance factor of node N> >getBalance(N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)>return> 0;> > >return> this>.height(N.left) ->this>.height(N.right);> >}> > >insert(node, key) {> >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node ==>null>)>return> new> Node(key);> > >if> (key node.left = this.insert(node.left, key); else if (key>node.key) node.right = this.insert(node.right, ключ); // Повторювані ключі заборонені else return node; /* 2. Оновити висоту цього вузла-предка */ node.height = 1 + this.max(this.height(node.left), this.height(node.right)); /* 3. Отримайте коефіцієнт балансу цього вузла-батька, щоб перевірити, чи цей вузол став незбалансованим */ var balance = this.getBalance(node); // Якщо цей вузол стає незбалансованим, тоді є // 4 випадки Ліворуч Лівий Регістр if (баланс> 1 && ключ повертає this.rightRotate(node); // Правий Правий Регістр якщо (баланс node.right.key) повертає це. leftRotate(node); // Left Right Case if (balance> 1 && key> node.left.key) { node.leftRotate(node.left); return this.rightRotate(node) } // Right Лівий регістр, якщо (баланс<-1 && key < node.right.key) { node.right = this.rightRotate(node.right); return this.leftRotate(node); } /* return the (unchanged) node pointer */ return node; } // A utility function to print preorder traversal // of the tree. // The function also prints height of every node preOrder(node) { if (node != null) { document.write(node.key + ' '); this.preOrder(node.left); this.preOrder(node.right); } } } // Driver code var tree = new AVLTree(); /* Constructing tree given in the above figure */ tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 40); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 25); /* The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ document.write( 'Preorder traversal of the ' + 'constructed AVL tree is ' ); tree.preOrder(tree.root);> |
>
java і swing
>Вихід
Preorder traversal of the constructed AVL tree is 30 20 10 25 40 50>
Аналіз складності
Часова складність: O(log(n)), для вставки
Допоміжний простір: О(1)
Операції обертання (обертання вліво і вправо) займають постійний час, оскільки там змінюється лише кілька вказівників. Оновлення висоти та отримання коефіцієнта балансу також займає постійний час. Таким чином, часова складність вставки AVL залишається такою ж, як і вставки BST, яка дорівнює O(h), де h є висотою дерева. Оскільки дерево AVL є збалансованим, висота дорівнює O(Logn). Отже, часова складність вставки AVL дорівнює O(Logn).
Порівняння з Red Black Tree:
Дерево AVL та інші самобалансуючі дерева пошуку, такі як Red Black, корисні для виконання всіх основних операцій за час O(log n). Дерева AVL більш збалансовані порівняно з червоно-чорними деревами, але вони можуть спричиняти більше обертань під час вставки та видалення. Отже, якщо ваша програма передбачає багато частих вставок і видалень, то слід віддати перевагу деревам Red Black. І якщо вставки та видалення відбуваються рідше, а пошук є більш частою операцією, то дереву AVL слід віддати перевагу, ніж Red Black Tree.
Нижче наведено повідомлення для видалення в дереві AVL:
Дерево AVL | Набір 2 (видалення)
