Дано корінь a Двійкове дерево пошуку і ціле число k . Завдання знайти найбільше число у бінарному дереві пошуку, тобто менше ніж або рівні до k, якщо такий елемент не існує, вивести -1.
приклади:
введення:
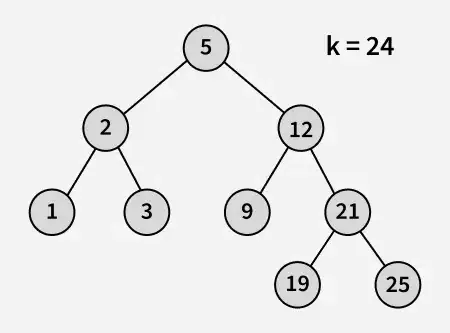
Вихід: 21
Пояснення: 19 і 25 є двома найближчими числами до 21, а 19 є найбільшим числом, яке має значення менше або дорівнює 21.
введення: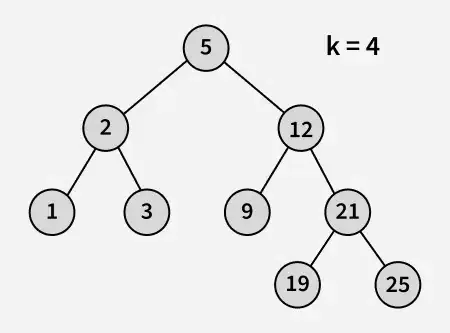
Вихід: 3
Пояснення: 3 і 5 є двома найближчими числами до 4, а 3 є найбільшим числом, яке має значення менше або дорівнює 4.
Зміст
- [Наївний підхід] Використання рекурсії - O(h) час і O(h) простір
- [Очікуваний підхід] Використання ітерації - O(h) час і O(1) простір
[Наївний підхід] Використання рекурсії - O(h) час і O(h) простір
C++Ідея полягає в тому, щоб почати з корінь і порівняйте його значення з k. Якщо значення вузла більше k, перейдіть до лівого піддерева. Інакше знайдіть значення найбільшого числа, менше ніж рівне k у праве піддерево . Якщо праве піддерево повертає -1 (це означає, що такого значення не існує), тоді повертається значення поточного вузла. Інакше повертає значення, яке повертає праве піддерево (оскільки воно буде більшим за значення поточного вузла, але меншим за k).
// C++ code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion #include
// Java code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int val) { data = val; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to find max value less than k static int findMaxFork(Node root int k) { // Base cases if (root == null) return -1; if (root.data == k) return k; // If root's value is smaller // try in right subtree else if (root.data < k) { int x = findMaxFork(root.right k); if (x == -1) return root.data; else return x; } // If root's data is greater // return value from left subtree. return findMaxFork(root.left k); } public static void main(String[] args) { int k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); System.out.println(findMaxFork(root k)); } }
# Python code to find the largest value # smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node: def __init__(self val): self.data = val self.left = None self.right = None # function to find max value less than k def findMaxFork(root k): # Base cases if root is None: return -1 if root.data == k: return k # If root's value is smaller # try in right subtree elif root.data < k: x = findMaxFork(root.right k) if x == -1: return root.data else: return x # If root's data is greater # return value from left subtree. return findMaxFork(root.left k) if __name__ == '__main__': k = 24 # creating following BST # # 5 # / # 2 12 # / / # 1 3 9 21 # / # 19 25 root = Node(5) root.left = Node(2) root.left.left = Node(1) root.left.right = Node(3) root.right = Node(12) root.right.left = Node(9) root.right.right = Node(21) root.right.right.left = Node(19) root.right.right.right = Node(25) print(findMaxFork(root k))
// C# code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion using System; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int val) { data = val; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to find max value less than k static int FindMaxFork(Node root int k) { // Base cases if (root == null) return -1; if (root.data == k) return k; // If root's value is smaller // try in right subtree else if (root.data < k) { int x = FindMaxFork(root.right k); if (x == -1) return root.data; else return x; } // If root's data is greater // return value from left subtree. return FindMaxFork(root.left k); } static void Main() { int k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); Console.WriteLine(FindMaxFork(root k)); } }
// JavaScript code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // function to find max value less than k function findMaxFork(root k) { // Base cases if (root === null) return -1; if (root.data === k) return k; // If root's value is smaller // try in right subtree else if (root.data < k) { let x = findMaxFork(root.right k); if (x === -1) return root.data; else return x; } // If root's data is greater // return value from left subtree. return findMaxFork(root.left k); } let k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 let root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); console.log(findMaxFork(root k));
Вихід
21
[Очікуваний підхід] Використання ітерації - O(h) час і O(1) простір
C++Ідея полягає в тому, щоб почати з корінь і порівняйте його значення з k . Якщо значення вузла дорівнює <= k оновити значення результату до кореневого значення та перейти до правильно піддерево ще перемістити до зліва піддерево. за ітеративно застосовуючи цю операцію до всіх вузлів, ми можемо мінімізувати простір, необхідний для рекурсія стек.
// C++ code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion #include
// Java code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int val) { data = val; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to find max value less than k static int findMaxFork(Node root int k) { int result = -1; // Start from root and keep looking for larger while (root != null) { // If root is smaller go to right side if (root.data <= k) { result = root.data; root = root.right; } // If root is greater go to left side else { root = root.left; } } return result; } public static void main(String[] args) { int k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); System.out.println(findMaxFork(root k)); } }
# Python code to find the largest value # smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node: def __init__(self val): self.data = val self.left = None self.right = None # function to find max value less than k def findMaxFork(root k): result = -1 # Start from root and keep looking for larger while root is not None: # If root is smaller go to right side if root.data <= k: result = root.data root = root.right # If root is greater go to left side else: root = root.left return result if __name__ == '__main__': k = 24 # creating following BST # # 5 # / # 2 12 # / / # 1 3 9 21 # / # 19 25 root = Node(5) root.left = Node(2) root.left.left = Node(1) root.left.right = Node(3) root.right = Node(12) root.right.left = Node(9) root.right.right = Node(21) root.right.right.left = Node(19) root.right.right.right = Node(25) print(findMaxFork(root k))
// C# code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion using System; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int val) { data = val; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to find max value less than k static int FindMaxFork(Node root int k) { int result = -1; // Start from root and keep looking for larger while (root != null) { // If root is smaller go to right side if (root.data <= k) { result = root.data; root = root.right; } // If root is greater go to left side else { root = root.left; } } return result; } static void Main() { int k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); Console.WriteLine(FindMaxFork(root k)); } }
// JavaScript code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // function to find max value less than k function findMaxFork(root k) { let result = -1; // Start from root and keep looking for larger while (root !== null) { // If root is smaller go to right side if (root.data <= k) { result = root.data; root = root.right; } // If root is greater go to left side else { root = root.left; } } return result; } let k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 let root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); console.log(findMaxFork(root k));
Вихід
21Створіть вікторину


