Python є мовою програмування з урахуванням регістру, що означає, що мова по-різному обробляє символи верхнього та нижнього регістру. Наприклад, у Python змінна 'x' не збігається зі змінною 'X'. Така поведінка відрізняється від деяких інших мов програмування, таких як JavaScript, які не враховують регістр.
У Python назви змінних, назви функцій і ключові слова чутливі до регістру. Це означає, що якщо ви визначите змінну «x», а потім спробуєте посилатися на неї як «X», Python розглядатиме її як іншу змінну, і ви отримаєте повідомлення про помилку. Так само, якщо ви спробуєте викликати функцію «print» замість «Print», Python також видасть вам помилку.
Ось приклад того, як чутливість до регістру впливає на імена змінних у Python:
x = 5 X = 10 print(x) # Output: 5 print(X) # Output: 10
Вихід
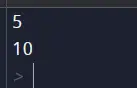
Пояснення:
У цьому прикладі ми визначили дві змінні, 'x' і 'X', з різними значеннями. Коли ми роздруковуємо їх, ми бачимо, що Python розглядає їх як окремі змінні та присвоює їм різні значення.
Чутливість до регістру також стосується імен функцій у Python. Наприклад:
список в java
print('Hello, World!') # Output: Hello, World! Print('Hello, World!') # Output: NameError: name 'Print' is not defined
Вихід

Пояснення:
вбудована функція 'print()' відрізняється від функції 'Print()'. Перший працюватиме належним чином, а другий видаватиме помилку, оскільки це не визначена функція.
Ключові слова в Python також чутливі до регістру. Це означає, що якщо ви використовуєте ключове слово, як-от «якщо» або «для», у нижньому регістрі, воно працюватиме належним чином. Однак, якщо ви використовуєте його у верхньому регістрі, Python розглядатиме його як назву змінної, і ви отримаєте помилку.
Вихідний код:
if x <10: print('x is less than 10') if x < 10: # output: nameerror: name 'if' not defined pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/48/is-python-case-sensitive-3.webp" alt="Is Python Case Sensitive"> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above code, we have created two if statements. In the first if statement, we have used the proper syntax as Python is case-sensitive. We have created the first if statement with small i, and the second if statement has a capital I which means it is not correct syntax, so it will throw an error.</p> <p>In addition to variable names, function names, and keywords, Python is also case-sensitive when it comes to file names. This means that the file 'example.txt' is different from the file 'Example.txt,' and the interpreter will treat them as separate files.</p> <p>It is important to keep in mind that Python is case-sensitive when naming variables, functions, and keywords. This can lead to errors and unexpected behavior if you're not careful. To avoid these issues, it is a good practice to use a consistent naming convention, such as using lowercase letters for all variable and function names.</p> <p>In conclusion, Python is a case-sensitive programming language. This means that the language treats uppercase and lowercase characters differently. This applies to variable names, function names, keywords, and file names. It's important to keep in mind that case sensitivity can lead to errors and unexpected behavior if you're not careful, so it's a good practice to use a consistent naming convention.</p> <hr></10:>