Дано прямокутний папір розмірів a x b . Завдання полягає в тому, щоб розрізати весь папір на мінімум кількість площі штук. Ми можемо вибрати квадратні частини будь-якого розміру, але їх потрібно розрізати не перекриваючи та не залишаючи додаткового простору .
приклади:
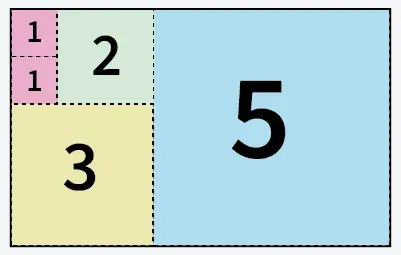
введення: a = 5 b = 8
5 квадратів, вирізаних з паперу розміром 5 х 8
Вихід: 5
Пояснення: Ми можемо розрізати папір на 5 квадратів: 1 квадрат розміром 5x5, 1 квадрат розміром 3x3, 1 квадрат розміром 2x2 і 2 квадрати розміром 1x1.введення: a = 13 b = 11
6 квадратів, вирізаних з паперу розміром 13 х 11
Вихід: 6
Пояснення: Ми можемо розрізати папір на 6 квадратів: 1 квадрат розміром 7x7, 1 квадрат розміром 6x6, 1 квадрат розміром 5x5, 2 квадрати розміром 4x4 і 1 квадрат розміром 1x1.підручник c#введення: a = 6 b = 7
5 квадратів, вирізаних з паперу розміром 6х7
Вихід: 5
Пояснення: Ми можемо розрізати папір на 5 квадратів: 1 квадрат розміром 4x4, 2 квадрати розміром 3x3 і 2 квадрати розміром 3x3.злиття, сортування java
Зміст
- [Неправильний підхід 1] Використання жадібної техніки
- [Неправильний підхід 2] Використання динамічного програмування
- [Правильний підхід] Використання DFS і динамічного програмування
[Неправильний підхід 1] Використання жадібної техніки
На перший погляд може здатися, що проблему можна легко вирішити, вирізавши з паперу найбільший можливий квадрат, а потім вирізавши найбільший квадрат із паперу, що залишився, і так далі, поки ми не виріжемо весь папір. Але це рішення невірне.
Чому Greedy Approach не працює?
Розглянемо папір розміром 6x7 тоді, якщо ми спробуємо жадібно розрізати папір, ми отримаємо 7 квадрати: 1 квадрат розміру 6x6 і 6 квадратів розм 1x1 тоді як правильне рішення: 5. Отже, жадібний підхід не спрацює.
[Неправильний підхід 2] Використання динамічного програмування
Динамічне програмування з вертикальними або горизонтальними розрізами: Іншим рішенням, яке може здатися правильним, є використання Динамічне програмування . Ми можемо підтримувати таблицю dp[][] так, щоб dp[i][j] = мінімальна кількість квадратів, які можна вирізати з паперу такого розміру i x j . Тоді для паперу розміру axb
- Ми можемо спробувати розрізати його вздовж кожного ряду: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i - k][j] + dp[k][j]) де k може бути в діапазоні [1 i - 1].
- Ми можемо спробувати розрізати його вздовж кожного стовпця: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i][j - k] + dp[i][k]) де k може бути в діапазоні [1 j - 1].
Нарешті, мінімум усіх скорочень буде відповіддю. Але це рішення теж невірне.
Чому вертикальне або горизонтальне розрізання за допомогою підходу динамічного програмування не працює?
Це не спрацює, оскільки ми припускаємо, що вертикальний або горизонтальний розріз завжди ділить прямокутник на дві частини. Розглянемо папір розміром 13x11 тоді, якщо ми спробуємо розрізати папір за допомогою підходу DP, ми отримаємо 8 квадратів, але правильна відповідь (як показано в прикладах) – 6. Отже, динамічне програмування не працюватиме.
[Правильний підхід] Використання DFS і динамічного програмування
C++The ідея це вирізати весь папір за допомогою ДФС в знизу вгору спосіб. У кожному кроці знайдіть нижній лівий кут паперу та спробуйте вирізати з цього кута квадрати всіх можливих розмірів. Вирізавши квадрат, знову знайдіть нижній лівий кут паперу, що залишився, щоб вирізати квадрати всіх можливих розмірів і так далі. Але якщо ми спробуємо всі можливі розрізи з нижнього лівого кута кожного можливого розміру паперу, це буде неефективно. Ми можемо оптимізувати його, використовуючи Динамічне програмування зберігати мінімальні відрізки для кожного можливого розміру паперу.
Щоб однозначно ідентифікувати будь-який розмір паперу, ми можемо підтримувати масив remSq[] таким чином, що remSq[i] зберігає кількість квадратів розміром 1x1, що залишилися, в i-му стовпці паперу. Отже, для паперу розміром 6x7 remSq[] = {6 6 6 6 6 6 6}. Крім того, щоб знайти нижній лівий кут, ми знайдемо перший індекс із максимальною кількістю квадратів, що залишилися. Тому ми можемо хешувати значення масиву remSq[], щоб знайти унікальний ключ для всіх можливих значень масиву remSq[].
java локальна датачас
// C++ Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb #include
// Java Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb import java.util.*; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int base = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Map<Integer Integer> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.containsKey(key)) return memo.get(key); int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = Arrays.copyOf(remSq b); int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo.put(key ans); return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; Arrays.fill(remSq a); Map<Integer Integer> memo = new HashMap<>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Sample Input int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb System.out.println(minCut(a b)); } }
# Python Program to find minimum number of squares to cut # from a paper of size axb # function to get the hash key for remSq array def getKey(remSq b): base = 1 key = 0 for i in range(b): key += remSq[i] * base base = base * (b + 1) return key # Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts # for a given remSq array def minCutUtil(remSq a b memo): # pointers to mark the start and end of range # with maximum remaining squares start = 0 # Check if we have previously calculated the answer # for the same state key = getKey(remSq b) if key in memo: return memo[key] maxRemSq = 0 # Find the starting point of min height for i in range(b): if remSq[i] > maxRemSq: maxRemSq = remSq[i] start = i # If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already # cut the entire paper if maxRemSq == 0: return 0 end = start newRemSq = remSq[:] ans = float('inf') # Find the ending point of min height while end < b: # length of edge of square from start till current end squareEdge = end - start + 1 # If the current column does not have maximum remaining # squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of # size squareEdge then break out of the loop if newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq or newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0: break # If we can cut a square of size squareEdge # update the remainingSquares for i in range(start end + 1): newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge # Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)) end += 1 memo[key] = ans return ans # Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut # using paper of size a X b def minCut(a b): # if the given rectangle is a square if a == b: return 1 # Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns remSq = [a] * b memo = {} return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) if __name__ == '__main__': # Sample Input a = 13 b = 11 # Function call to get minimum number # of squares for axb print(minCut(a b))
// C# Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int baseVal = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * baseVal); baseVal = baseVal * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Dictionary<int int> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.ContainsKey(key)) return memo[key]; int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = (int[])remSq.Clone(); int ans = int.MaxValue; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.Min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) remSq[i] = a; Dictionary<int int> memo = new Dictionary<int int>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } static void Main() { int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb Console.WriteLine(minCut(a b)); } }
// JavaScript Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb // function to get the hash key for remSq array function getKey(remSq b) { let base = 1; let key = 0; for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array function minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares let start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state let key = getKey(remSq b); if (key in memo) return memo[key]; let maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq === 0) return 0; end = start; let newRemSq = remSq.slice(); let ans = Infinity; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end let squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] !== maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (let i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b function minCut(a b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a === b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns let remSq = new Array(b).fill(a); let memo = {}; return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } // Driver Code let a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb console.log(minCut(a b));
Вихід
6
Часова складність: O(a^b) для кожного з b стовпців ми можемо мати квадрати.
Допоміжний простір: O(a^b) завдяки запам'ятовуванню кожного унікального стану.

 5 квадратів, вирізаних з паперу розміром 5 х 8
5 квадратів, вирізаних з паперу розміром 5 х 8 6 квадратів, вирізаних з паперу розміром 13 х 11
6 квадратів, вирізаних з паперу розміром 13 х 11 5 квадратів, вирізаних з паперу розміром 6х7
5 квадратів, вирізаних з паперу розміром 6х7